The Competition
Local Brain Bees
The local Brain Bee level is comprised of grassroots chapters, which are generally organized through universities or research institutions in cities, states, provinces, or other geographic regions. Each local chapter, and also each region’s local chapters, are organized individually, so format may vary.
Prepare
Most Brain Bee local competitions are based on either the Brain Facts or Neuroscience: The Science of the Brain books. These are brief, introductory materials that offer an introduction to neuroscience. However, please note that each local Brain Bee is organized individually. Please contact your local Brain Bee for specific information as to how the competition will be run, and how to prepare.
National Brain Bees
Each National Brain Bee is organized individually. Please contact your region’s coordinator for more information regarding your National Brain Bee. The winners of the National Brain Bees qualify to participate in the IBB World Championship.
International Brain Bee
The IBB World Championship is designed to be a high-level and friendly academic competition.
In order to qualify for the World Championship, students need to win the highest level of Brain Bee competition in their country/region.
The material draws from university and medical school course content and requires thoughtful preparation. All participants are expected to support one another throughout the experience, during and between contest sections.
The IBB organizers reserve the right to amend the details of the competition at any stage.
Competition Sections
Upon qualification for the competition, student participants will receive extended and updated rules and study material for each competition section from their National Coordinators.
The rules and materials are prepared, updated and provided yearly by the Academic and Competition Advisory Committee (ACAC).
At the start of each section, competitors will be provided with an overview of the rules. Each section has a defined time-limit per question.
Neuroanatomy
During the neuroanatomy exam, students will either work with whole and sectioned human brains or with detailed graphical illustrations. For each of the major brain structures, knowledge about the anatomical position, the origin of the main input fibres, the destination of main output fibres, grey matter nuclei, white matter tracts, the main neuronal types and their connectivity and the main functions are required.
More information
During the Neuroanatomy Section, students should be prepared to be quizzed on any structure featured in the IBB study guide. No list/word bank will be provided during the competition.
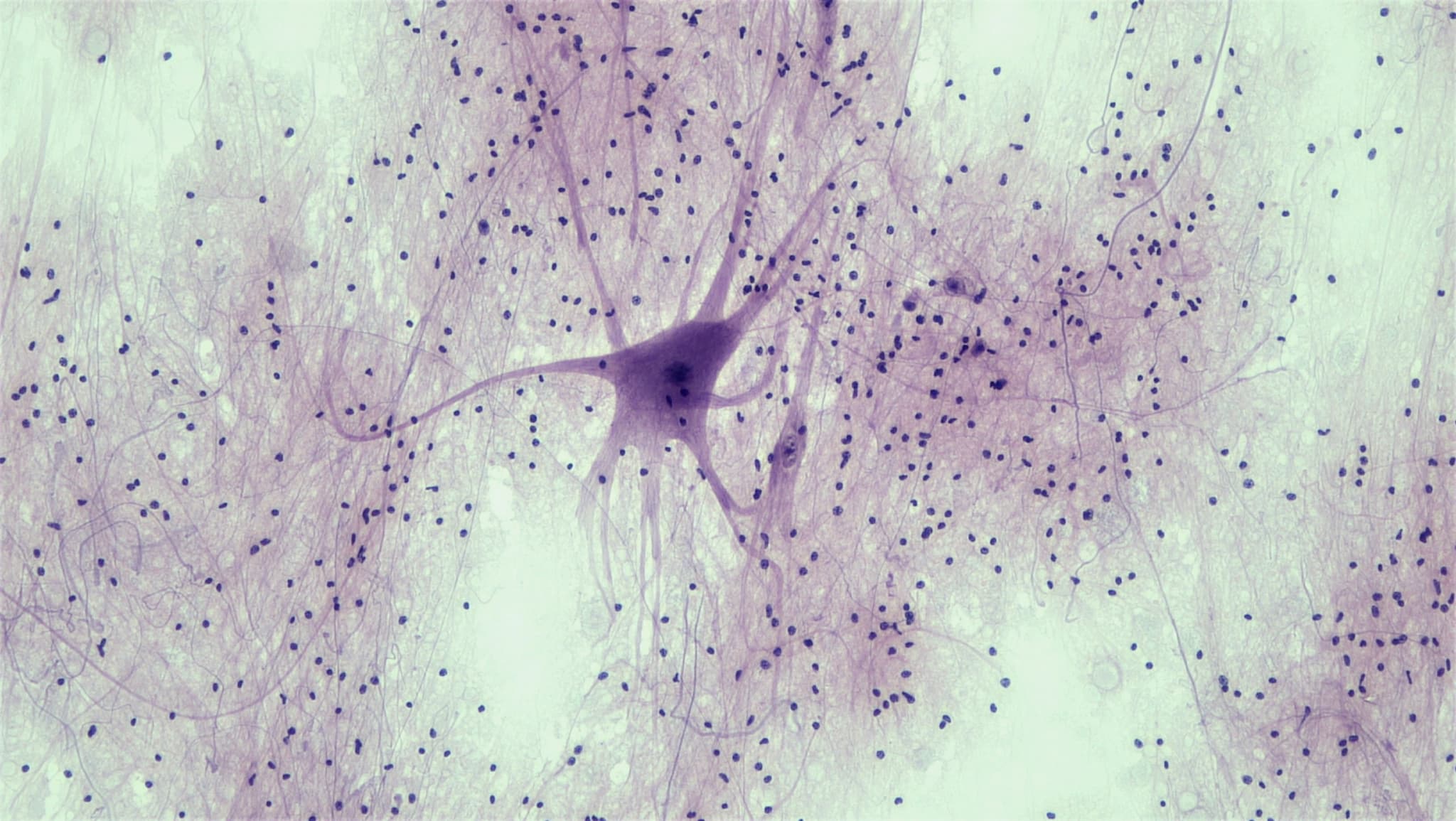
Neurohistology
During the neurohistology section human tissues will be displayed under microscopes or students will be provided with representative captured images. Students must identify the structures by name and/or describe the basic functions of the tissue.
More information
There will be microscope slides, each with a thin section of any of the human tissues stated in the IBB study guide. Students should be prepared to identify the structures and substructures, the origin of the main input fibres, the destination of the main output fibres, and function of the displayed celltype/ tissue by name.
Written Test
The written exam is comprised of a multiple-choice and short-answer test. The questions cover the entire materials of the study guide curriculum.
More information
Above each question, there is an indication if it is a single-choice question (only one answer is correct) or if multiple answers may be selected.
Patient Diagnosis
Video footage of patients will be shown alongside a written medical history. Students may request results from three lab or imaging exams to aid in the diagnosis.
More information
The Patient Diagnosis Section consists of videos of patients, each with one of the possible neurological disorders listed below. The video will portray motor and/or other visual symptoms of the patient, and a brief written history, as told by the patient, will be provided. Each disorder will be presented in a common form (no rare forms of the disorders). Upon choosing three diagnostic tests, the students will be asked to diagnose the patient.
Diagnostic Tests
1 Neuroimaging
1.1 CT scan (x-ray Computed Tomography)
1.2 PET and SPECT (Single Photon/Positron Emission Computed Tomography) 1.3 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
2 Neurophysiological Tests
2.1 EEG (Electroencephalography)
2.3 NCS (Nerve Conduction Study)
3 Cognitive Measures
4 Biofluid-based biomarkers
4.1 – Blood-based biomarkers
4.2 – CSF-based biomarkers
Neurological Disorders
1 Genetic Disorders
1.1 Rett Syndrome (RTT)
1.2 Down Syndrome (DS)
1.3 Familial Hemiplegic Migraine (FHM)
1.4 Huntington’s Disease (HD)
1.5 Fragile X syndrome
2 Infection
2.1 Meningitis
2.2 Prion Disease
2.3 Tetanus
3 Degenerative Diseases
3.1 Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
3.2 Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
3.3 Frontotemporal dementia
3.4 Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
4 Vascular Disorders
4.1 Stroke
4.1 Vascular dementia
5 Psychiatric Disorders
5.1 Depression
5.2 Schizophrenia (SCZ)
5.3 Bipolar Affective Disorders (BD)
5.4 Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASDs)
5.5 Anxiety disorder
5.6 Obsessive compulsive disorder
5.7 Post-traumatic stress disorders
5.8 Personality disorders
5.9 Eating disorders
6 Structural Defects
6.1 Hydrocephalus
7 Generalized diseases of muscle or peripheral nerves
7.1 Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
7.2 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
7.3 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
8 Trauma
8.1 Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
8.2 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
9. Peripheral nerve injury
The effects of injury to the spinal accessory nerve, spinal nerves C5, T2, L4, L5, radial nerve, median nerve, ulnar nerve, femoral nerve, sciatic nerve.
10 Epilepsy
11 Tourette’s Syndrome (TS)
12 Neurodevelopmental Diseases
12.1 Infantile Cerebral Palsy (ICP)
12.2 Spina Bifida
12.3 Down Syndrome
12.4 Attention Deficit Disorder (ADHD)
13 Addiction and Substances of Abuse
13.1 Alcohol addiction – Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (WKS)
13.2 Drug addiction
Live Judging
Once, the National Champions competed in the first four exam parts. The top performers will qualify for the Live Judging Session. During this session, the judging panel will pose questions to the group. Students are given 30-90 seconds to write and log in their answers. Each answer will be individually reviewed and scored by the judging panel.
More information
The Live Judging Session is designed as an elimination round. For each wrongly answered question, the student gets a strike. After two strikes, the student is disqualified. The session continues until only one competitor is left.
Scores are distributed based on how many questions were answered correctly.
Sample questions
All questions are formatted to require answers that are either one word or a short phrase.
- Which neurotransmitter is released by motor neurons that facilitate voluntary movements? Acetylcholine
- How many axons can be myelinated by a single Schwann cell? One
Prepare
Rules and Assistive Tools Overview
The International Brain Bee expects a high standard of integrity from each student participant. Absolutely zero tolerance will be demonstrated toward acts of cheating, which will result in immediate elimination from the contest. The event will be conducted professionally and in a way that fosters a positive and fair experience for everyone. Student contestants will be given more thorough rules as the competition date approaches.
Contestants may bring their personal writing instruments, such as pens, pencils, erasers, and pencil sharpeners, into the examination rooms. For students from non-English speaking backgrounds, a translation dictionary without any notes may also be used. All translation dictionaries will be checked before exam sections.
Not permitted are mobile phones, programmable calculators, other electronic devices, or any other written materials. Posession of such items in restricted areas may result in immediate disqualification.
Prizes
All competitors will receive a Certificate of Accomplishment. In addition, the top three winners will receive a monetary award and a medal. Partners also provide additional awards.
1st Place
- $3,000 USD
- Personalized plaque
2nd Place
- $2,000 USD
3rd Place
- $1,000 USD
IBB Neuroanatomy/ Histology Award
The IBB Neuroanatomy/ Histology Award* will recognize the top student in the neuroanatomy/ neurohistology component of the IBB World Championship. The award recognises the importance of neuroanatomy/ histology to understanding the brain. It consists of a US $100 prize and a book featuring the work of Nobel Laureate Santiago Ramȯn Y Cajal and his contributions to neuroscience through his artistic brain imagery.
*The award was established with a donation from Linda J. Richards, Chair of the
Department of Neuroscience and Edison Professor of Neuroscience at Washington
University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Dr. Richards has served on the IBB’s Board of Directors and is a longstanding supporter of the Brain Bee initiative and the Founder of the Australian Brain Bee Challenge.
Please be advised that aspects of the competition may vary from year to year.
